loon's displays that are based on Cartesian coordinates (i.e. scatterplot, histogram and graph display) allow for layering visual information including polygons, text and rectangles. Every layer has a unique id and the layer with the plot model (i.e. scatterplot points, histogram or graph) is called the model layer and has the id model.
The available layer types are the following
and n dimensional state or compound layers
n circles (with size state)n stringsn polygonsn rectanglesn linesNote that for polygons, rectangles and lines the states x and y have a non-flat data structure
, i.e. a nested list
$p layer polygons -x {{1 2 3} {4 2 1 3} {1 2 3 4 1}}\
-y {{2 1 3} {2 1 4 3} {2 1 4 3 2}}\
-color {red red blue}\
-active {T F T}\
-selected {T T T}Some important implementation details for working with layers are
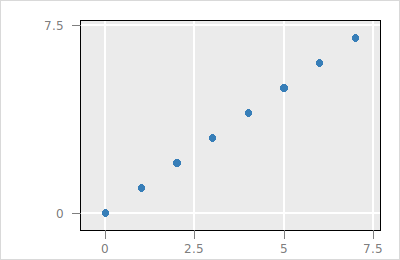
group layer can be a parent to children layers (any of the above mentioned layer types). The tree root has id root.n can not be set to 1. Use the singular version instead (e.g. text).In this section we layer information onto the following scatterplot
set p [plot -x {0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7} -y {0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7}\
-showScales TRUE -showGuides TRUE]
The layer ids sub-command returns the plot's layer ids
$p layer ids
#% root modelThe root and model layer exist in all plots. The root layer is the tree root and the model layer represents the visual representation of the data for the specific plot (e.g. histogram, scatterplot or graph).
The following code layers a polygon
set l_p [$p layer polygon -x {0 1 2 3 3 2.5 1.5 0}\
-y {5 4.5 4.5 5 7 7 5.5 5.2}\
-color black -linecolor orange\
-linewidth 5]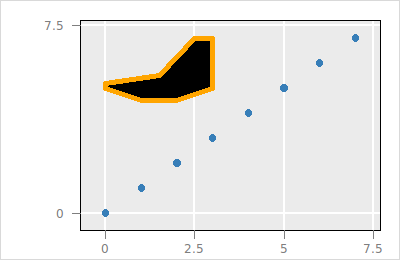
The variable l_p holds the layer id. You can get the state descriptions similar as with normal plots
$p layer use $l_p info statesOther layer types can be layered similarly, e.g.
set l_l [$p layer line -x {0 2.5 5 7.5}\
-y {4.5 0 6 3}\
-linewidth 4\
-color red]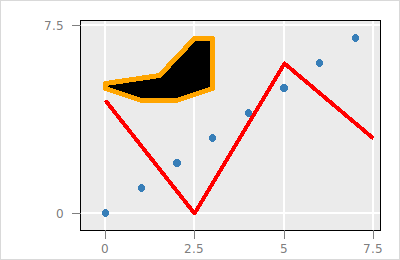
The layers are arranged in a tree structure and the rendering is according to the Depth-First algorithm of the visual layers in the tree. For example, we can layer a rectangle over the previous layers:
set l_r [$p layer rectangle\
-x {0.5 6.5} -y {0.5 6.5} -color green -linecolor '']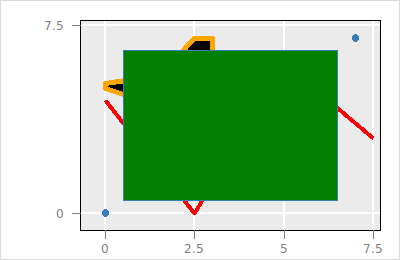
The rectangle with the layer id saved in the l_r variable over-plots the other layers, i.e. it is rendered last. To get a printout of the tree structure run
$p layer printTree
#% layer2
#% layer1
#% layer0
#% modelHence the topmost layer, i.e. layer2, is rendered last. Layers can be moved with the layer move function as follows
$p layer move $l_r root end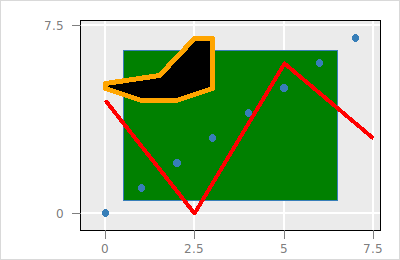
Note, that the parent layer, the index specifying the location among the parents children layers, and the label of a layer can also be specified when adding a layer. However parent, index and label are not states of the layer, instead they are information for the layer collection.
The following code creates a group and moves the polygon layer and line layer into it
set l_g [$p layer group -parent root -index end]
$p layer move $l_l $l_g end
$p layer move $l_p $l_g end
$p layer printTree
#% layer3
#% model
#% layer2
#% +layer3
#% layer1
#% layer0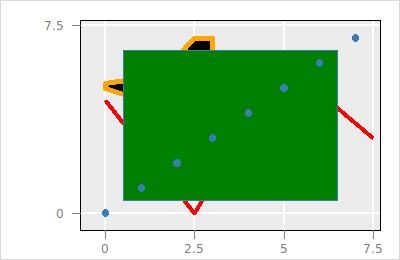
To move a layer one position up or down (i.e. change place with a sibling) one can also use the layer raise and layer lower sub command, respectively.
The visibility of a layer can be changed with the hide and show sub-command .
$p layer hide $l_g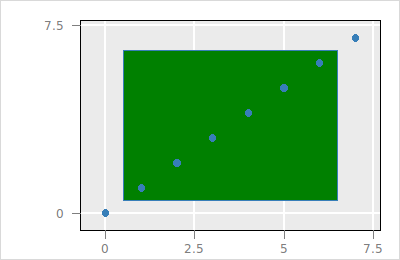
and
$p layer show $l_g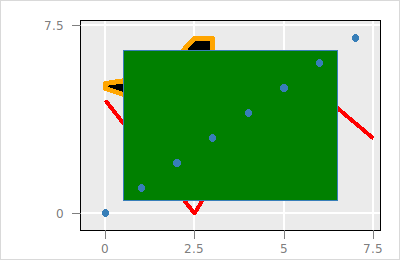
The layer with the rectangle can be deleted as follows
$p layer delete $l_r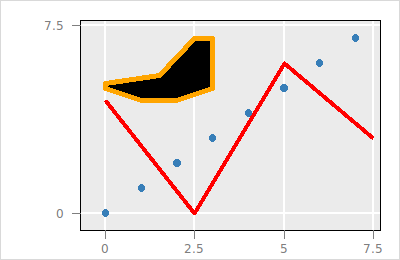
If a group layer gets deleted with layer delete then all its children layers get moved into their grandparent group layer. To delete a group layer and all it's children use the layer expunge subcommand.
$p layer expunge $l_g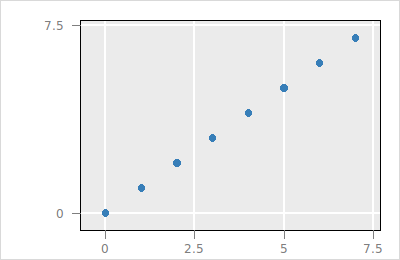
It is also possible zoom and pan such that a particular layer fills the plot region
set l_o [$p layer oval -x {2.5 5} -y {2.5 5} -color thistle -index end]
$p scaleto layer $l_o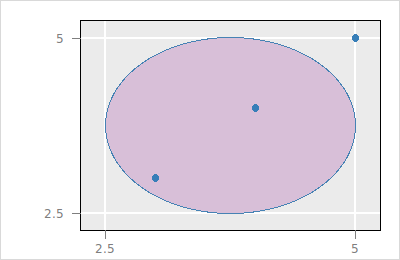
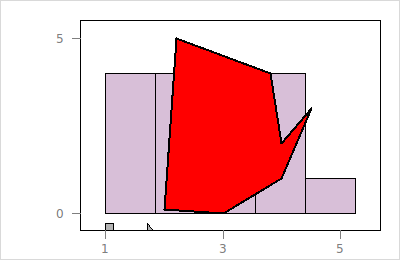
To modify the layer states works as described for plot states here. We start with the following histogram with a polygon layer:
set h [histogram -x {1 1 2 1 4 3 2 2 1 4 5 4 3 2 4 3}\
-binwidth 0.85 -showScales TRUE -showLabels FALSE]
set l_p [$h layer polygon -x {2 3 4 4.5 4 3.8 2.2}\
-y {0.1 0 1 3 2 4 5}\
-color steelblue -linecolor '']
$h scaleto world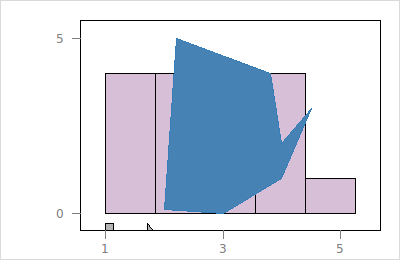
To query the state information use
$h layer use $l_p info statesA layer state is queried as follows:
$h layer use $l_p -colorA layer state is configured as follows:
$h layer use $l_p configure -color red -linecolor black -linewidth 2